The 10 countries with the fastest-declining population

The global population, once predicted to grow indefinitely, is now facing a significant shift as birth rates decline and aging populations increase.

While some regions continue to experience rapid population growth, others are witnessing a decline, raising concerns about economic stability, labor shortages, and the sustainability of social welfare systems.
This demographic shift is reshaping economies, societies, and global power dynamics.
Global population decline
Several factors contribute to population decline in various regions worldwide. One of the primary causes is declining fertility rates, with many countries falling below the replacement level of 2.1 children per woman.
Economic challenges, urbanization, and shifting social norms have led to fewer people choosing to have large families.
According to Statista, Europe is the continent experiencing the most significant population decline, with its population shrinking by 0.2% in 2023.
The continent also has the highest number of countries (six) among the 10 fastest-shrinking nations, including Greece, San Marino, and Belarus, as well as Balkan nations Bosnia and Herzegovina, Albania, and Kosovo.
This trend is driven by aging populations, low birth rates, and high emigration rates, leading to long-term demographic and economic challenges.
Meanwhile, Africa and parts of South Asia continue to grow rapidly, with countries like Nigeria, Ethiopia, and India seeing high birth rates. However, even in these regions, urbanization and economic changes may slow population growth in the coming decades.
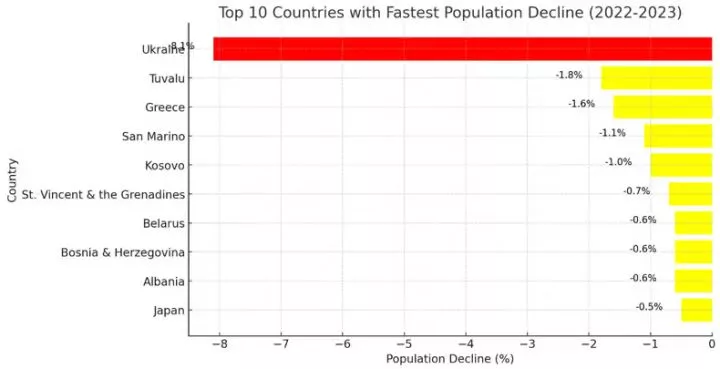
The table below presents data on the nations experiencing the highest rates of population decline between 2022 and 2023, based on figures from the UN Population Division.
| 1 | Ukraine | -8.10% |
| 2 | Tuvalu | -1.80% |
| 3 | Greece | -1.60% |
| 4 | San Marino | -1.10% |
| 5 | Kosovo | -1.00% |
| 6 | St. Vincent & the Grenadines | -0.70% |
| 7 | Belarus | -0.60% |
| 8 | Bosnia & Herzegovina | -0.60% |
| 9 | Albania | -0.60% |
| 10 | Japan | -0.50% |
Key Insights from the Chart
Ukraine’s Sharp Decline (-8.1%)
-
Ukraine experienced the most significant population drop at -8.1%, largely due to the ongoing war and the mass exodus of refugees following Russia’s invasion in 2022.
-
This decline is driven by emigration, deaths from the conflict, and a low birth rate.
Other Countries with Noticeable Declines
-
Tuvalu (-1.8%): A small island nation facing climate-related migration, where rising sea levels are forcing residents to relocate.
-
Greece (-1.6%): A long-term declining birth rate, economic struggles, and emigration of young workers contribute to its shrinking population.
-
San Marino (-1.1%) & Kosovo (-1.0%): These small European states face demographic decline due to low fertility rates and emigration trends.
Declining Populations in the Caribbean and Europe
-
St. Vincent & the Grenadines (-0.7%): Economic migration to larger economies like the U.S. and Canada is a key factor.
-
Belarus (-0.6%) and Bosnia & Herzegovina (-0.6%): Both countries face depopulation due to emigration, aging populations, and low birth rates.
-
Albania (-0.6%): Young Albanians continue to migrate to Western Europe for better job opportunities.
Japan’s Population Decline (-0.5%)
-
Japan has long struggled with an aging population, low fertility rates, and limited immigration, causing its steady population decrease.
Population Trends by Continent
-
Europe (-0.2%): The only continent experiencing an overall population decline, mainly due to aging populations and lower birth rates.
-
North America (+0.6%) & Asia (+0.6%): Moderate growth driven by immigration (in North America) and sustained, though slowing, birth rates (in Asia).
-
Latin America & the Caribbean (+0.7%): Modest population growth despite emigration trends in some countries.
-
Oceania (+1.1%): Stronger growth, likely due to immigration and higher birth rates in countries like Australia and Papua New Guinea.
-
Africa (+2.3%): The highest growth rate, with high fertility rates across the continent continuing to drive population increases.





